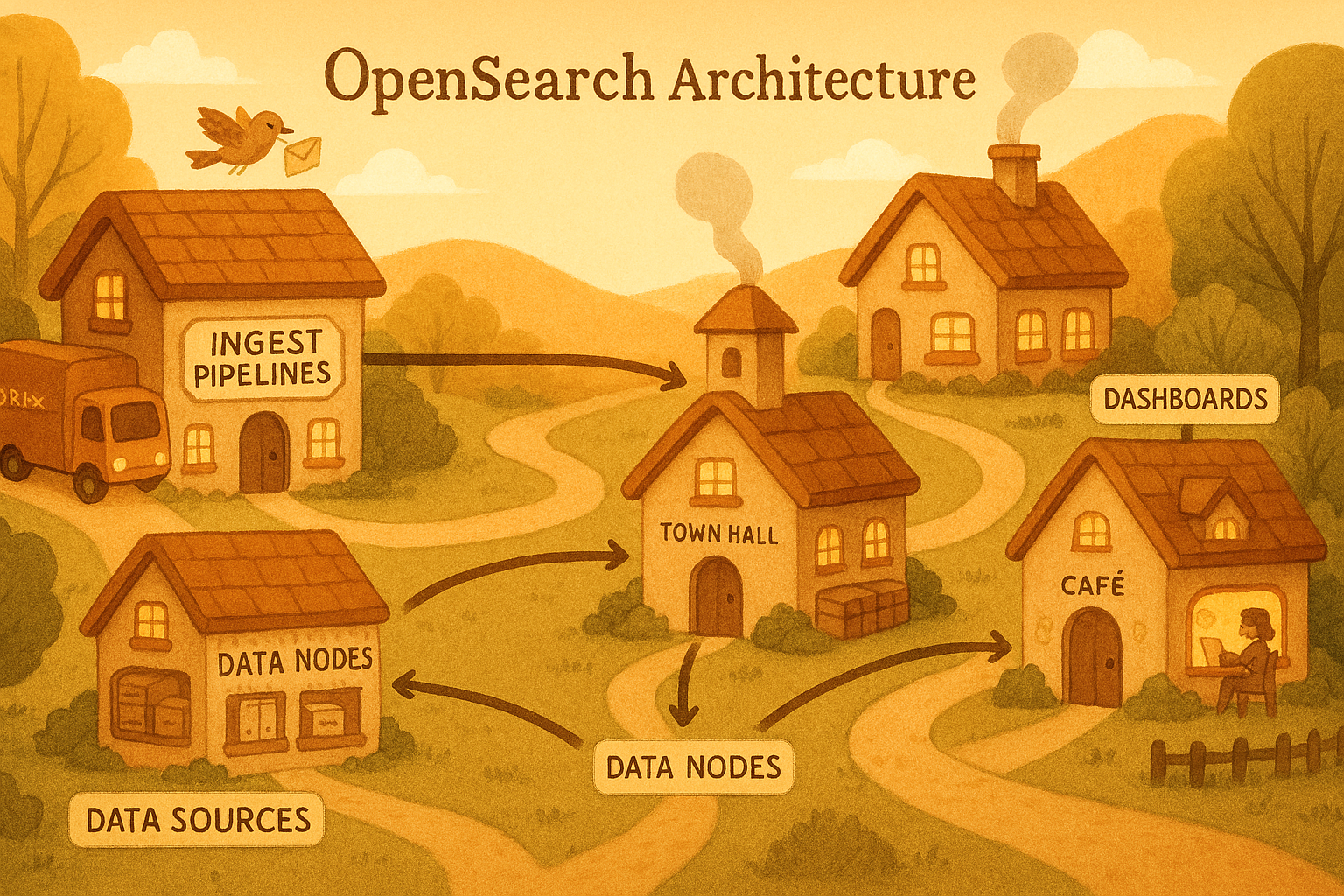
Reindexing in OpenSearch: A Step-by-Step Guide
Hello, fellow developers and data enthusiasts! If you’ve ever worked with search engines like OpenSearch (the open-source fork of Elasticsearch), you know that managing indices is a core part of th...

Hello, fellow developers and data enthusiasts! If you’ve ever worked with search engines like OpenSearch (the open-source fork of Elasticsearch), you know that managing indices is a core part of th...

In today’s data-driven landscape, the ability to search, analyze, and visualize massive volumes of data in real-time has become essential for successful digital operations. OpenSearch stands at the...

Revolutionizing Asset Management Through Graph-Based Ownership Networks: A Complete Technical Guide In today’s interconnected financial landscape, understanding true asset exposure and ownership s...
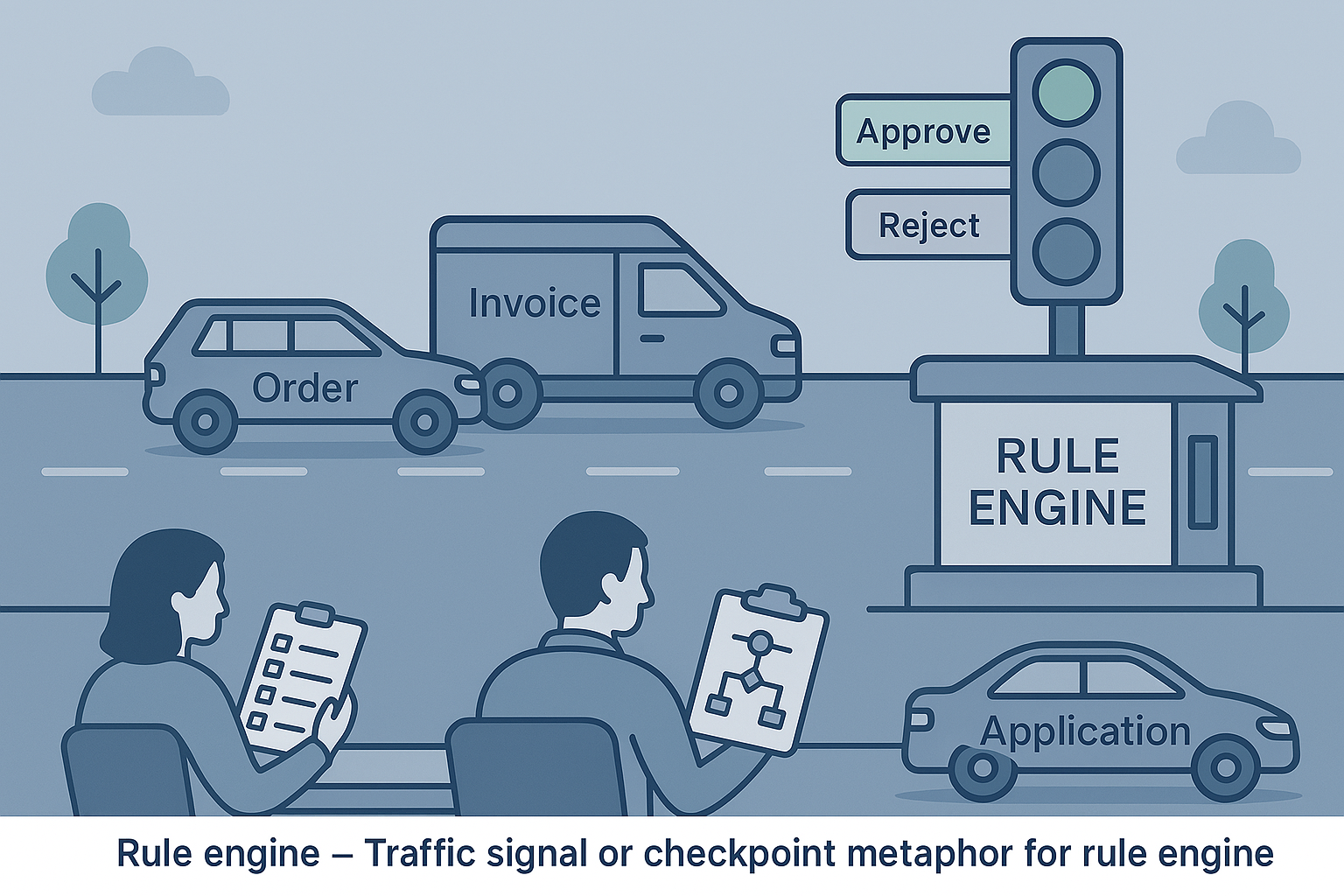
Continuing our journey from flexible validation to agile, on-demand rule execution, powered by API endpoints Table of Contents Introduction: From Pipeline to Precision The Challenge: Dynamic...

Making the leap from Java to Python development can feel like learning a new language—because it literally is! But beyond syntax changes, one of the most significant adjustments involves adapting y...

How we evolved our rule engine to support intelligent conditional execution, failure isolation, and business-aware decision trees The Evolution: From Sequential to Intelligent Conditional Executio...

How we evolved our rule engine to support dynamic staging, configuration-driven execution, and enterprise data quality pipelines Table of Contents Introduction: Beyond Basic Validation The...

How we transformed scattered validation logic into a maintainable, scalable rule engine that powers modern applications Table of Contents Introduction: The Hidden Cost of Scattered Business ...

Overview This guide demonstrates how to leverage PostgreSQL’s native AWS S3 integration to directly export and import table data between your database and Amazon S3 - all through SQL commands exec...
Scalability is a critical aspect of modern web services, especially as user bases grow and traffic increases. In this blog series, we’ll break down the key concepts of scalability into digestible p...